The global supply chain has experienced a dramatic shift in recent years, fueled by the rise of e-commerce, labor shortages, global crises, and ever-increasing consumer expectations. In response, industries across the board from logistics and manufacturing to construction and engineering are investing heavily in robotics and automation. But this evolution is not just about mechanization; it’s about building intelligent systems that can think, adapt, and scale.
The future of logistics robotics lies at the intersection of hardware precision, software intelligence, and operational agility. Robotics is no longer limited to repetitive, preprogrammed tasks it now encompasses autonomous decision-making, real-time learning, and collaborative operation. This article explores how robotics is transforming not only logistics but also manufacturing, construction, and artificial intelligence itself, forging a future where humans and machines collaborate seamlessly to build smarter, more resilient systems.
Future of Robotics in Manufacturing
Manufacturing has historically been the primary adopter of industrial robots and the future promises even greater transformation. As global production shifts toward customization, speed, and quality, robotics is becoming more flexible, intelligent, and human-aware.
One major trend is the rise of collaborative robots (cobots) machines designed to work alongside humans, sharing tasks rather than replacing them. Unlike traditional robots that require cages and separation, cobots use sensors and AI to interact safely in shared spaces, supporting complex assembly, quality control, or packaging tasks.
Another key development is adaptive automation. Rather than relying on static programming, robots are learning to respond to environmental variables adjusting grip strength, tool orientation, or movement paths in real time. This is especially useful in high-mix, low-volume production where variability is the norm.
Data also plays a crucial role in the future of manufacturing robotics. Digital twins, for example, allow manufacturers to simulate robotic workflows in virtual environments before deploying them physically reducing downtime and improving accuracy. When integrated with machine vision and predictive maintenance algorithms, robotic systems become self-optimizing, reducing errors and increasing uptime.
Manufacturing will continue to lead in robotic integration, but the systems of the future will be smarter, more agile, and more integrated with enterprise-wide digital infrastructure.
Future of Robotics in Logistics
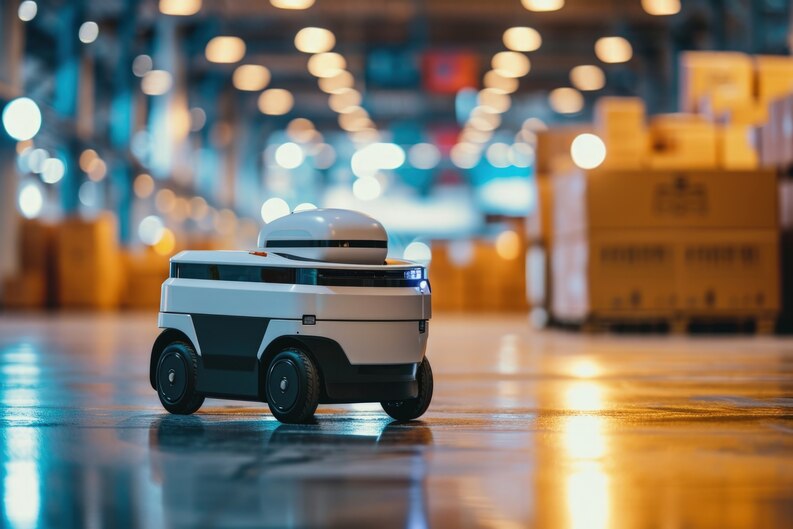
The logistics sector is perhaps experiencing the fastest and most profound transformation due to robotics. As warehousing, fulfillment, and transportation systems face mounting pressure to be faster, more accurate, and more scalable, robots are becoming essential infrastructure.
The future of logistics robotics involves fully autonomous supply chains. In smart warehouses, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) will manage everything from shelf-to-person picking to inter-zone transfers. These robots will operate on self-generated maps, adapt to real-time obstructions, and collaborate as a coordinated fleet.
Meanwhile, automated sortation systems powered by machine vision will accelerate the handling of parcels, reducing processing time from minutes to seconds. In shipping yards and ports, robotic cranes and shuttles will manage container loading and unloading with centimeter-level precision guided by AI algorithms that optimize for speed, weight distribution, and departure times.
Even transportation will be redefined. Self-driving trucks and delivery drones are expected to play a greater role, especially for last-mile logistics, where flexibility and speed are critical. The integration of robotics with IoT (Internet of Things) platforms will allow operators to monitor cargo conditions in transit, adjust routes on the fly, and reduce environmental impact through real-time optimization.
By 2030, it’s estimated that over 75% of large logistics centers will implement advanced robotics systems, transforming logistics from a labor-heavy industry to a data-driven, autonomous network of intelligent machines.
The Future of Robotics in Construction
Construction, historically considered one of the most labor-intensive and risky industries, is now undergoing a technological awakening and robotics is at the center of it.
Robots in construction are already handling tasks like bricklaying, concrete pouring, road painting, and structural inspection. As capabilities grow, we will see the rise of mobile robotic units capable of navigating uneven terrain, adapting to on-site conditions, and working collaboratively with human crews.
Key innovations in construction robotics include:
- 3D printing robots, capable of building full-scale structures layer by layer using concrete or composite materials. This not only reduces waste but also shortens construction timelines.
- Inspection drones and crawling bots that assess bridge integrity, scan building façades, and monitor infrastructure without putting human lives at risk.
- Robotic exoskeletons worn by workers to reduce fatigue and improve lifting capability, thereby minimizing injury and increasing productivity.
The combination of robotics and Building Information Modeling (BIM) will enable machines to follow digital blueprints directly, translating design files into real-world construction tasks. This will fundamentally change how buildings are planned and built, paving the way for automated, modular construction techniques that reduce cost and environmental footprint.
As cities expand and labor becomes scarcer, robotics will help meet growing infrastructure demands while ensuring greater safety, consistency, and sustainability.
The Future of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
Perhaps the most transformative shift in robotics is its growing integration with artificial intelligence. While traditional robots were limited to predefined tasks, the next generation of machines will be context-aware, predictive, and decision-capable.
AI in robotics means machines can:
- Interpret visual and sensor data
- Learn from past actions
- Collaborate with humans dynamically
- Optimize themselves based on goals and constraints
In logistics, AI-powered robots will no longer just follow routes they’ll predict inventory bottlenecks, respond to urgent orders, and even negotiate storage placement with other systems. In manufacturing, AI will allow robots to recognize flawed components, adjust tooling in real time, or switch tasks autonomously when production plans change.
AI also brings natural language interfaces, allowing operators to interact with robots using voice or text, eliminating the need for complex programming. This democratizes robotics, making them accessible even to smaller businesses or teams without deep technical expertise.
Crucially, AI allows for cross-domain learning. A robot trained in warehouse navigation can share insights with another operating in a construction yard. This interconnectivity will accelerate innovation and pave the way for multi-purpose robotic platforms that adapt to multiple environments.
The long-term convergence of robotics and AI will redefine not just how we work but how we design, build, distribute, and collaborate across the entire industrial value chain.
Conclusion
The future of logistics robotics is not just about machines it’s about creating intelligent, responsive, and scalable systems that empower industries to meet global demands with speed, precision, and sustainability. As robotics expands beyond its manufacturing roots into logistics, construction, and AI-powered environments, the possibilities are endless.
From autonomous mobile robots to construction printers and self-learning systems, robotics is becoming an integral part of our physical world. It enhances productivity, reduces risk, and makes operations more resilient against disruption. For organizations willing to invest strategically, the future of robotics is not just an upgrade it’s a competitive edge, a growth engine, and a pathway to intelligent infrastructure.